Forex trading for beginners can feel overwhelming at first. New
traders are often confronted with unfamiliar terms, fast-moving prices, and a
market that operates around the clock. At Pipdemy, we approach Forex education
differently. We believe learning works best when concepts are explained
clearly, practiced in a safe environment, and reinforced through
experimentation rather than pressure or hype.
The Forex market plays a real and
important role in the global economy. It exists to facilitate international
trade, investment, and currency exchange. Retail traders participate in this
market on a much smaller scale, with the goal of understanding how currency
prices change and managing risk responsibly. This article is designed to help
beginners and early intermediate traders build a solid foundation. There are no
shortcuts here. Instead, you will learn how the market actually works, step by
step.
In this guide, you will learn what
Forex trading is, how currency pairs work, how price movement is measured, and
why market sessions matter. You will also be introduced to the mindset Pipdemy
promotes: learning through demo trading, structured practice, and, when
appropriate, AI-assisted experimentation rather than guesswork.
To begin any serious journey into
Forex, it is essential to clearly understand what is forex trading and
what it is not.
Forex trading is the act of exchanging
one currency for another at an agreed price. Unlike stock markets, where you
buy shares of a company, Forex trading always involves two currencies at the
same time. When you trade, you are expressing a view about the relative
strength or weakness of one currency compared to another.
For example, if you believe the euro
will strengthen against the US dollar, you might buy the EUR/USD currency pair.
If the euro rises relative to the dollar, the value of that position increases.
If it falls, the position loses value.
The Forex market exists primarily to
support:
- International trade (companies exchanging currencies
to pay for goods and services)
- Global investment flows (investors moving capital
between countries)
- Risk management and hedging (protecting against
unfavorable exchange rate changes)
Retail trading is a small component of
this ecosystem. Understanding this helps beginners avoid unrealistic
expectations. Forex is not designed to make people rich quickly. It is a
financial market where skill, discipline, and risk control matter over time.
Forex does not have a single physical
exchange. Trading happens electronically between banks, financial institutions,
brokers, and individual traders. This decentralized structure is why the market
operates 24 hours a day during the business week, following the sun across
major financial centers.
For beginners, this means
flexibility, but also responsibility. You are not required to trade constantly.
In fact, learning when not to trade is just as important as knowing when
to participate.
A core concept in Forex is
understanding how currency pairs work. Every trade involves buying one
currency while selling another simultaneously.
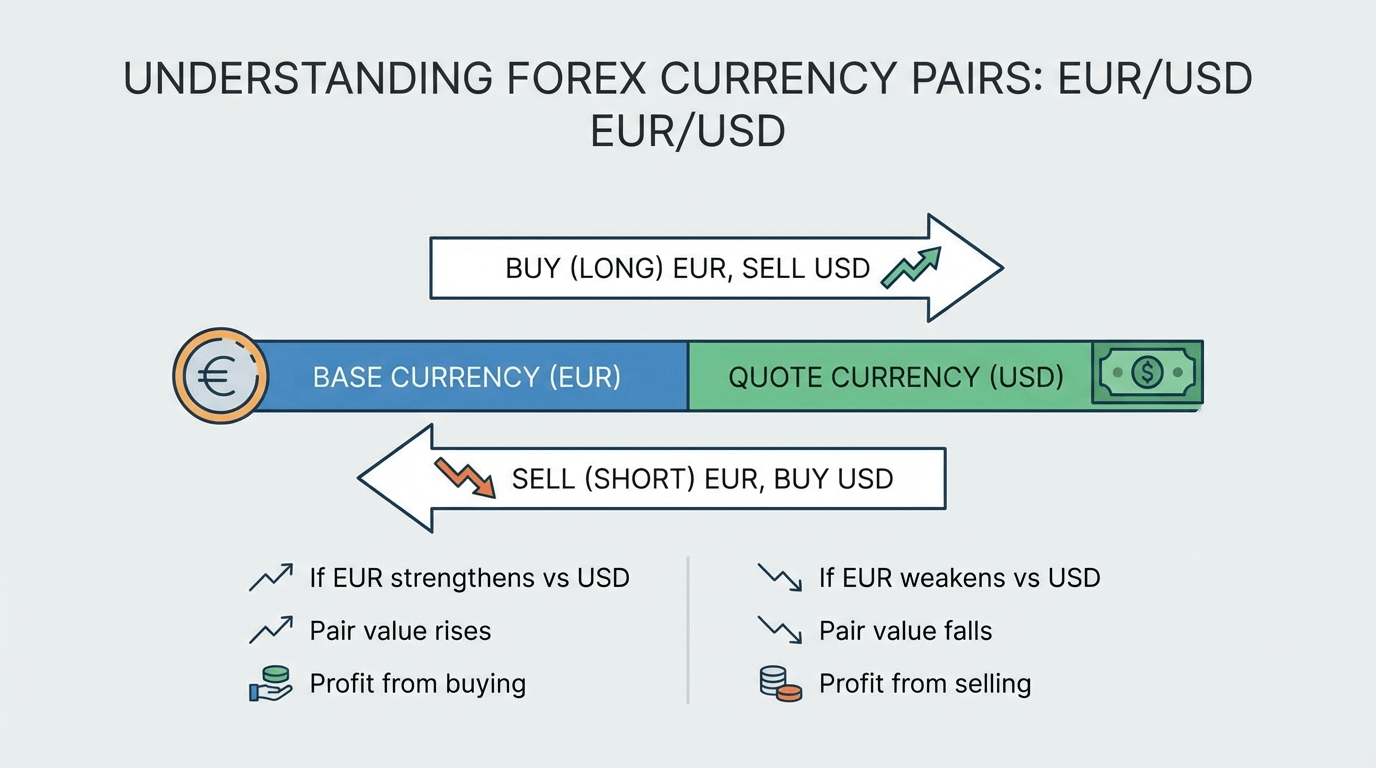
Each currency pair has two components:
• The base currency, which appears first
• The quote currency, which appears second
If a currency pair is quoted as EUR/USD at 1.1000, it means one euro is worth 1.10 US dollars. The price answers a simple question: how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency?
When you trade:
• Buying the pair means you expect the base currency to strengthen
• Selling the pair means you expect the base currency to weaken
Currency pairs are grouped based on
liquidity and global significance.
- Major pairs include currencies from the
world’s largest economies and always involve the US dollar.
- Minor pairs do not include the US dollar but
still involve widely traded currencies.
- Exotic pairs combine a major currency with one
from a smaller or emerging economy.
For beginners, major pairs are usually
easier to understand and trade. They tend to have more predictable behavior,
lower transaction costs, and more educational material available.
At Pipdemy, most educational examples
and demo exercises start with major pairs. This allows learners to focus on
understanding market behavior without unnecessary complexity.
To trade responsibly, you must understand how forex prices move and why markets change direction.
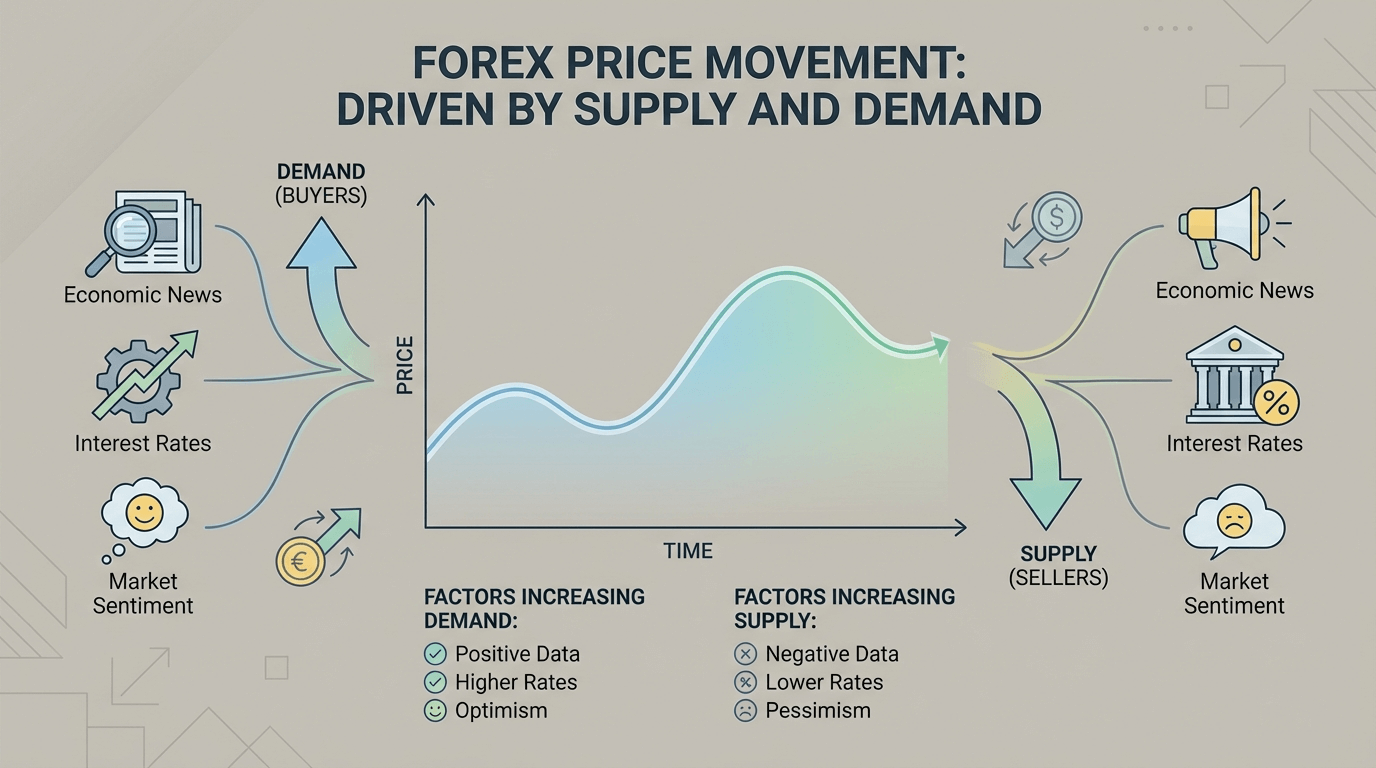
At the most basic level, currency prices move because of supply and demand. When demand for a currency increases relative to another, its value rises. When demand weakens, its value falls.
This demand is shaped by many factors, including:
• Economic growth
• Interest rates
• Inflation expectations
• Political stability
• Market sentiment and expectations
Prices often move not on current conditions alone, but on expectations about the future. A central bank hinting at future policy changes can move markets even before anything officially happens.
Beginners are often surprised to see
prices move in a direction that seems to contradict the news. This usually
happens because the market had already priced in the information. Understanding
this dynamic takes time and exposure to real market behavior.
This is why Pipdemy emphasizes demo
trading and replay-based learning. Observing price reactions without financial
risk helps learners develop realistic expectations and avoid emotional
decision-making.
Two of the most important measurement
concepts in Forex are price movement and position size. This is where pips
and lots explained becomes essential knowledge.
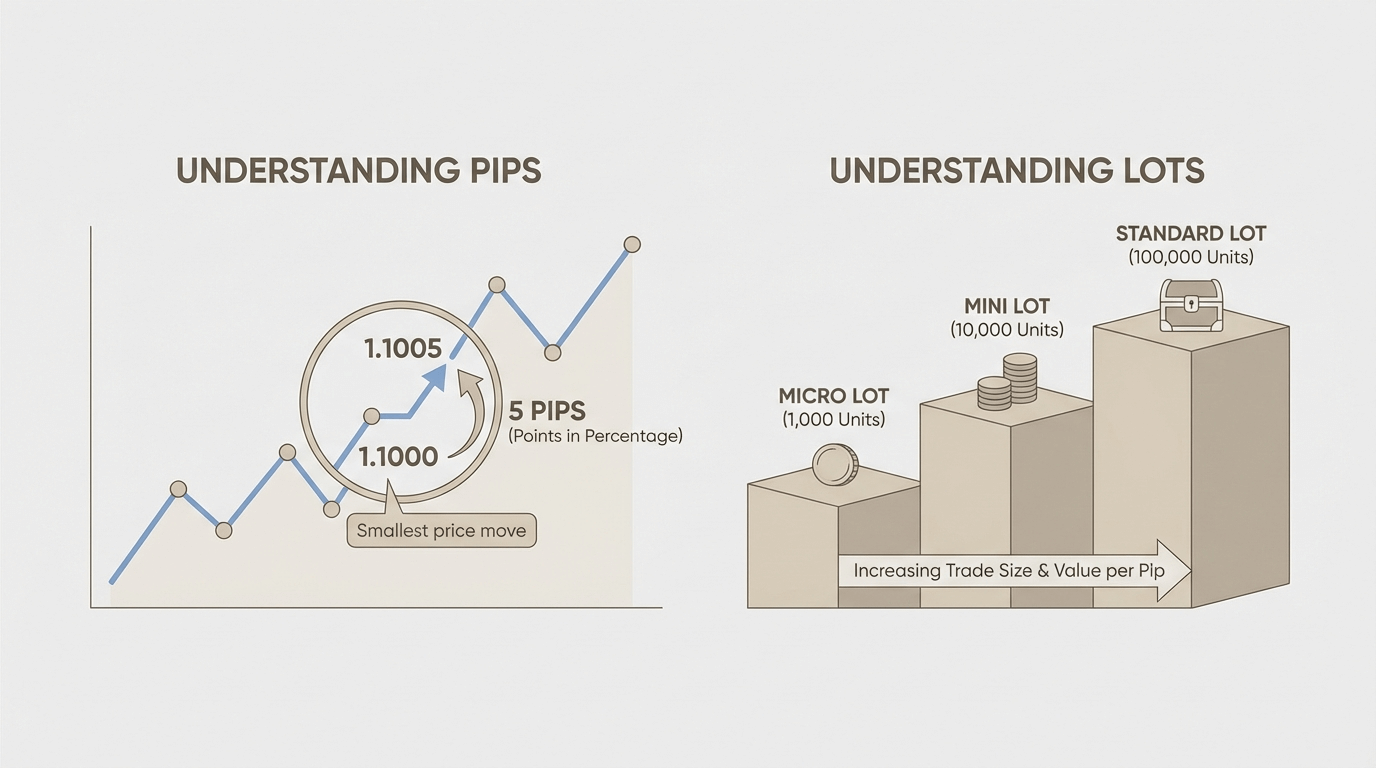
A pip is a standardized unit used to
measure price changes in a currency pair. For most pairs, one pip equals a
movement in the fourth decimal place. For example, a move from 1.1000 to 1.1001
is one pip.
Pips allow traders to measure gains,
losses, and risk in a consistent way across trades. Whether you are trading
large or small amounts, pips provide a shared language for understanding
movement.
A lot represents the size of your
trade. It determines how much exposure you have to price movement.
Common lot sizes include:
- Standard lots
- Mini lots
- Micro lots
Beginners often underestimate how
important lot size is. Two traders can see the same price movement in pips and
have very different outcomes based on how large their position is.
At Pipdemy, learners are encouraged to
start with the smallest possible position sizes in demo environments. This
builds awareness of risk before any real capital is involved.
Learning Forex without practice is like
learning to drive by reading a manual alone. Demo trading allows beginners to
experience real market conditions without real financial consequences.
Demo accounts simulate live prices and
trading execution. They allow learners to:
- Practice placing trades
- Observe how prices behave during different market
conditions
- Test ideas without emotional pressure
At Pipdemy, demo trading is not treated
as a casual sandbox. It is structured as a learning laboratory. Learners are
guided to form simple hypotheses, test them repeatedly, and review results
objectively. This approach aligns naturally with AI-assisted analysis and
experimentation introduced later in the learning path.
For a structured approach to building
these foundational skills, Pipdemy integrates learning paths that connect
theory to practical experimentation through -.
Because Forex is global, understanding forex
market sessions explained is critical for timing and awareness.
The market is generally divided into
four major sessions:
- Sydney
- Tokyo
- London
- New York
Each session reflects the business
hours of its respective financial center. When one session closes, another
opens, keeping trading continuous.
Different sessions have different
characteristics:
- Some are more active
- Some have higher volatility
- Some see tighter or wider spreads
When sessions overlap, trading activity
often increases. This can lead to faster price movement but also higher risk.
Beginners benefit from observing these patterns in demo accounts before
attempting to trade them.
At Pipdemy, learners are taught that
activity does not equal opportunity. Sometimes the best decision is to wait for
clearer conditions rather than trade every session.
A strong mindset is just as important
as technical knowledge. Beginner traders often struggle not because they lack
intelligence, but because they lack structure and patience.
Some typical issues include:
- Trading too frequently
- Increasing position size after losses
- Chasing price instead of planning trades
- Ignoring risk limits
These behaviors are not signs of
failure. They are part of the learning curve. What matters is creating a system
that encourages reflection instead of emotional reactions.
Pipdemy emphasizes slow, deliberate
progress:
- Learn one concept at a time
- Practice it in a controlled environment
- Review results honestly
- Improve incrementally
AI tools, when used correctly, support
this process by helping traders analyze patterns and outcomes objectively. They
do not replace thinking or decision-making. They enhance feedback and learning
efficiency.
Learning Forex becomes much easier once
the language of the market feels familiar. A clear forex terminology
glossary helps beginners follow educational material, analyze charts, and
understand trading platforms without confusion. Below are essential terms
explained in simple, practical language.
- Bid price is the price at which the market is willing to buy
a currency pair.
- Ask price is the price at which the market is willing to sell
a currency pair.
The difference between these two prices
is called the spread. Beginners often overlook the spread, but it represents a
real trading cost that affects every position.
The spread is the gap between
the bid and ask price. Some currency pairs have tighter spreads due to higher
liquidity, while others are more expensive to trade. Understanding spreads
matters because a trade starts slightly negative due to this cost.
Leverage allows traders to control a larger
position with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage increases potential
gains, it also magnifies losses. For beginners, leverage should be approached
with caution and used conservatively, especially during the learning phase.
Margin is the amount of money required to
open and maintain a leveraged trade. It is not a fee, but a portion of your
account set aside as collateral. If losses grow too large, positions may be
closed automatically to prevent further losses.
Volatility refers to how much and how quickly
prices move. Highly volatile conditions can create opportunities, but they also
increase risk. Beginners often confuse volatility with opportunity, when in
reality it requires careful risk control.
Slippage happens when an order is executed at a
different price than expected, usually during fast market movements. It is a
normal part of live trading and something beginners should be aware of before
transitioning from demo to real accounts.
One of the most important lessons in Forex
trading for beginners is that learning how to manage risk matters more than
finding winning trades.
Many beginners focus heavily on market
direction while ignoring risk. This often leads to short-lived success followed
by significant losses. In reality, even experienced traders cannot predict the
market with certainty. What they can control is how much they risk on each
trade.
At Pipdemy, risk management is
introduced early and reinforced constantly. The goal is to survive long enough
to learn, not to win every trade.
Risk is closely tied to position size.
Trading larger lots than your account can reasonably support increases emotional
pressure and reduces decision quality. Starting small allows beginners to think
clearly and focus on process rather than fear.
A common educational principle is
risking only a small percentage of capital on any single trade. This keeps
losses manageable and protects the learning account from large drawdowns.
Losses are part of trading. The key
difference between productive learners and frustrated beginners is
interpretation. Productive learners treat losses as feedback. They review
execution, market conditions, and decision logic instead of reacting
emotionally.
Pipdemy encourages learners to track
trades, label mistakes, and test alternatives in demo environments. This
transforms losses into educational data points.
Reading about Forex concepts is
necessary, but it is not enough. Knowledge becomes useful only when tested in
real market conditions.
Demo trading allows learners to
practice without financial consequences. However, its value depends on how it
is used. Random trading teaches little. Structured experimentation teaches a
lot.
At Pipdemy, demo trading is framed as a
laboratory:
- Form a simple idea
- Test it repeatedly
- Record outcomes
- Adjust based on evidence
This experimental mindset prepares
traders for more advanced tools, including AI-assisted analysis, which relies
on data quality and disciplined testing.
AI does not replace thinking. It
supports it. When used responsibly, AI can help beginners identify patterns,
review trade behavior, and detect recurring mistakes. However, AI tools work
best when traders already understand the basics of price movement, risk, and
market structure.
This is why Pipdemy emphasizes
foundational education first. Without understanding concepts like pips, lots,
and sessions, AI outputs become confusing or misleading.
A sustainable Forex journey requires
structure. Jumping between strategies or copying trades without understanding
creates confusion rather than skill.
A healthy learning path typically
includes:
- Understanding market basics
- Practicing execution in demo accounts
- Learning simple risk management rules
- Reviewing results objectively
- Gradually increasing complexity only when ready
Pipdemy structures education around
this progression. Learners are encouraged to master each layer before moving
forward.
In Forex, patience itself is a skill.
Many losses come not from poor ideas, but from acting too early or too often.
Learning to wait for clarity and confirmation is part of becoming consistent.
This mindset separates
education-focused traders from those driven by urgency and emotion.








